|
Concentrator Photovoltaics, Concentrate Solar Energy
In telecommunications, the term concentrator has the following meanings: * In data transmission, a functional unit that permits a common data link, path to handle more data sources than there are channels currently available within the path. A concentrator usually provides communication capability between many low-speed, usually asynchronous channels and one or more high-speed, usually Synchronization, synchronous channels. Usually different speeds, codes, and protocols can be accommodated on the low-speed side. The low-speed channels usually operate in contention (telecommunications), contention and require buffering. * A device that connects a number of links with only one destination, the main function of this device is to make a kind of Load balancing (computing), load balancing between two or more servers connected together, data distribution is done according to the server processing rate. * A patch panel or other component in the cable plant where cable runs converge. * Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PPPoE
The Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a network protocol for Encapsulation (networking), encapsulating Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) frames inside Ethernet frames. It appeared in 1999, in the context of the boom of DSL as the solution for tunneling protocol, tunneling network packet, packets over the DSL connection to the ISP's Internet Protocol, IP network, and from there to the rest of the Internet. A 2005 networking book noted that "Most DSL providers use PPPoE, which provides authentication, encryption, and Data compression, compression." Typical use of PPPoE involves leveraging the PPP facilities for authenticating the user with a username and password, via the Password Authentication Protocol, PAP protocol or via Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol, CHAP. PAP was dominant in 2007 but service providers have been transitioning to the more secure CHAP, because PAP is a plain-text protocol. Around 2000, PPPoE was also starting to become a replacement meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentrating Solar Power
Concentrated solar power (CSP, also known as concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal) systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight into a receiver. Electricity is generated when the concentrated light is converted to heat (solar thermal energy), which drives a heat engine (usually a steam turbine) connected to an electrical power generator or powers a thermochemical reaction. As of 2021, global installed capacity of concentrated solar power stood at 6.8 GW. As of 2023, the total was 8.1 GW, with the inclusion of three new CSP projects in construction in China and in Dubai in the UAE. The U.S.-based National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), which maintains a global database of CSP plants, counts 6.6 GW of operational capacity and another 1.5 GW under construction. Comparison between CSP and other electricity sources As a thermal energy generating power station, CSP has more in common with thermal power st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
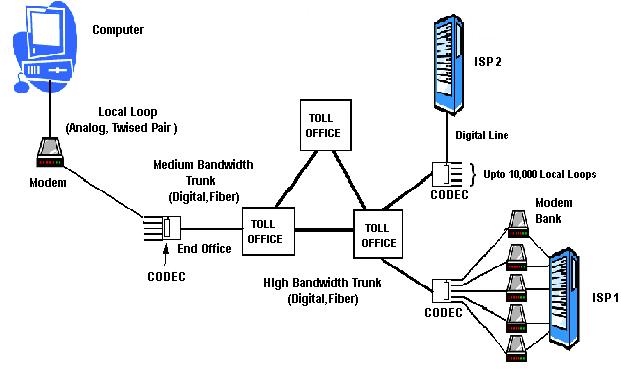
Remote Concentrator
In modern telephony a remote concentrator, remote concentrator unit (RCU), or remote line concentrator (RLC) is a concentrator at the lowest level in the telephone switch hierarchy. Subscribers' analogue telephone/PSTN lines are terminated on concentrators. They have three main functions: * Digitize: convert voice (and sometimes data) from analogue to a digital form. * Connect off-hook lines to the local exchange—the concentration function. * Multiplex, interleaving many calls together on a single wire or optical fiber. via Web Archive Only a few hundred telephone lines attach to each remote concentrator. In North America concentrators are loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Concentrator
An oxygen concentrator is a device that concentrates the oxygen from a gas supply (typically ambient air) by selectively removing nitrogen to supply an oxygen-enriched product gas stream. They are used industrially, to provide supplemental oxygen at high altitudes, and as medical devices for oxygen therapy. Oxygen concentrators are used widely for oxygen provision in healthcare applications, especially where liquid or pressurized oxygen is too dangerous or inconvenient, such as in homes or portable clinics, and can also provide an economical source of oxygen in industrial processes, where they are also known as oxygen gas generators or Oxygen plant, oxygen generation plants. Two methods in common use are pressure swing adsorption and membrane gas separation. Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) oxygen concentrators use a molecular sieve to adsorb gases and operate on the principle of Pressure swing adsorption#Rapid PSA, rapid pressure swing adsorption of atmospheric nitrogen onto zeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Hub
An Ethernet hub, active hub, network hub, repeater hub, multiport repeater, or simply hub is a network hardware device for connecting multiple Ethernet devices together and making them act as a single network segment. It has multiple input/output (I/O) ports, in which a signal introduced at the input of any Computer port (hardware), port appears at the output of every port except the original incoming. A hub works at the physical layer. A repeater hub also participates in collision detection, forwarding a jam signal to all ports if it detects a collision (telecommunications), collision. In addition to standard 8P8C ("RJ45") ports, some hubs may also come with a BNC connector, BNC or an Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) connector to allow connection to legacy 10BASE2 or 10BASE5 network segments. Hubs are now largely obsolete, having been replaced by network switches except in very old installations or #Uses, specialized applications. As of 2011, connecting network segments by repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Optical Network
A passive optical network (PON) is a fiber-optic telecommunications network that uses only ''unpowered'' devices to carry signals, as opposed to electronic equipment. In practice, PONs are typically used for the '' last mile'' between Internet service providers (ISP) and their customers. In this use, a PON has a point-to-multipoint topology in which an ISP uses a single device to serve many end-user sites using a system such as 10G-PON or GPON. In this one-to-many topology, a single fiber serving many sites branches into multiple fibers through a passive splitter, and those fibers can each serve multiple sites through further splitters. The light from the ISP is divided through the splitters to reach all the customer sites, and light from the customer sites is combined into the single fiber. Many fiber ISPs prefer this system. Components and characteristics A passive optical network consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office (hub), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (i.e., colors) of laser light. This technique enables bidirectional communications over a single strand of fiber (also called wavelength-division duplexing) as well as multiplication of capacity. The term WDM is commonly applied to an optical carrier, which is typically described by its wavelength, whereas frequency-division multiplexing typically applies to a radio carrier, more often described by frequency. This is purely conventional because wavelength and frequency communicate the same information. Specifically, frequency (in Hertz, which is cycles per second) multiplied by wavelength (the physical length of one cycle) equals velocity of the carrier wave. In a vacuum, this is the speed of light (usually denoted by the lowercase letter, c). In glass fiber, velocity is substant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Play (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, triple play is the provision of broadband internet, television, and telephony over a single connection. This approach emphasizes the supplier convergence of multiple services, aiming to enhance user convenience and streamline service delivery. CATV By about 2000, cable TV companies were in a technical position to offer ''triple play'' over one physical medium to a large number of their customers, as their networks already had sufficient bandwidth to carry hundreds of video channels. Cable's main competition for television in North America came from satellites, which could not compete for voice and interactive broadband due to the latency imposed by physical laws on a geosynchronous satellite—sometimes up to one full second of delay between speaking and being heard. Cable's main competition for voice and Internet access came from telcos, which were not yet able to compete for television in most markets because DSL over most local loops could not provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Concentrator
In modern telephony a remote concentrator, remote concentrator unit (RCU), or remote line concentrator (RLC) is a concentrator at the lowest level in the telephone switch hierarchy. Subscribers' analogue telephone/PSTN lines are terminated on concentrators. They have three main functions: * Digitize: convert voice (and sometimes data) from analogue to a digital form. * Connect off-hook lines to the local exchange—the concentration function. * Multiplex, interleaving many calls together on a single wire or optical fiber. via Web Archive Only a few hundred telephone lines attach to each remote concentrator. In North America concentrators are loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Loop
In telephony, the local loop (also referred to as the local tail, subscriber line, or in the aggregate as the last mile) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the common carrier or telecommunications service provider's network. At the edge of the carrier access network in a traditional public telephone network, the local loop terminates in a circuit switch housed in an incumbent local exchange carrier or telephone exchange. Infrastructure Traditionally, the local loop was an electrical circuit in the form of a single pair of conductors from the telephone on the customer's premises to the local telephone exchange. Single-wire earth return lines had been used in some countries until the introduction of electric tramways from the 1900s made them unusable. Historically the first section was often an aerial open-wire line, with several conductors attached to porcelain insulators on cross-arms on "te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers. The term "central office" can also refer to a central location for fiber optic equipment for a fiber internet provider. In historical perspective, telecommunication terminology has evolved with time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. A central office is defined as the telephone switch controlling connections for one or more central office prefixes. However, it also often denotes the building used to house the inside plant equipment for multiple telephone exchange areas. In North America, the term ''wire center'' may be used to denote a central office location, indicating a facility that provides a telephone with a dial tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |